We wanted to update our blog to help create a better understanding of GDPR in 2020 going into 2021. We will be discussing how this affects U.S. companies, the risks of failing to comply, how you can stay in compliance, and the progress of similar bills in America. So let’s dive into understanding how the GDPR is changing the world, data collection, and how this affects companies in America.
What Is The GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) became effective on May 25, 2018. The GDPR is designed to strengthen privacy protection for consumers within the European Union by broadening and clearly defining the obligations of companies to protect personal information.
How Does This Affect U.S. Companies?
The GDPR applies to all businesses that collect personal information from EU residents, including companies located within the EU and outside of the EU. In other words, if you collect personal data from residents of the EU, your business could be subject to the provisions of the GDPR, even if the business itself is not based out of the EU. If your business is located in the United States, but you offer products or services overseas, you need to ensure you are GDPR compliant. Data processors in the United States should also verify if they are subject to the privacy protections in the GDPR.
How Seriously Are Companies Taking GDPR Compliance?
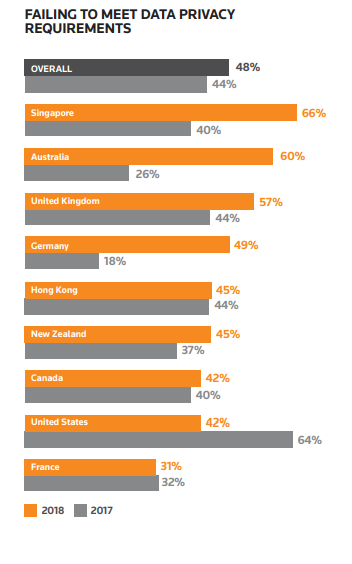
Based on the information provided by Thomson Reuters in their 2017-2018 survey, many companies are failing to either reach compliance or to stay in compliance. American companies, on the other hand, are actually the second most compliant country, surpassed only by France. To get a better look at who is compliant, you can view the graph to the right.
Many companies seem to be struggling with GDPR compliance as a whole. But, that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t take compliance seriously. This isn’t expected to go away anytime soon, and the momentum to pass similar regulations in America is gaining strength.
What Kind Of Penalties Occur If I Break Compliance?
The penalties for breaking compliance or simply ignoring compliance are steep. The fines for breaching GDPR can range from $11,934,450 or 2% of your company’s annual revenue (whichever is higher) to $23,868,900 or 4% of your company’s annual revenue (again, whichever is higher).
What Is A Data Subject?
The direct definition given by the GDPR articles defines a Data Subject as the following:
“personal data’ means any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘data subject’); an identifiable natural person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identifier such as a name, an identification number, location data, an online identifier or to one or more factors specific to the physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural or social identity of that natural person.”
Does This Affect EU Citizens Living In America?
No, the GDPR only applies to how companies collect data on EU Citizens living in the EU. So GDPR protections do not extend to EU citizens living in America.
What About U.S. Citizens in the EU?
Only if the U.S. citizen is living in the EU at the time of data collection. U.S. citizens in America are not protected from data collection from companies based out of the E.U.
What Should My First Steps Be When Becoming Compliant?
Consent
Most companies understand that they need to obtain consent from an individual before collecting personal data. However, under the GDPR, your privacy policy explaining how you collect information and what information you collect may not be sufficient. You may need to adjust your policies to comply with the GDPR consent requirements for EU citizens.
Deletion of Personal Information
The GDPR contains provisions that require companies to erase or delete personal information under certain circumstances. For example, if your business does not need the information any longer and is not required legally to maintain the information, you need a process in place for ensuring that the information is erased “without undue delay.” Companies must have procedures in place that determine when deleting personal information is required and for deleting the information in accordance with the GDPR requirements.
Data Breaches
You may already have robust procedures in place for protecting the personal data you collect; however, these procedures may not comply with all of the GDPR requirements. For example, the GDPR requires companies to report a personal data breach within 72 hours of the breach. Companies should examine their incident response plans and other data security guidelines to ensure they are GDPR compliant.
Does It Matter If I’m Considered A Controller or Processor?
First, let’s clarify what both of these terms mean. Controllers collect the personal data of data subjects, while processors handle the personal data collected by the controllers. Both must follow GDPR guidelines. So even though your company processes the data properly under GDPR guidelines, if the company that you’ve partnered with breaks a guideline, you will both be liable.
Who Enforces These Guidelines?
GDPR compliance is monitored and enforced by the European Commission. But if a company fails to maintain compliance and is outside of the jurisdiction of the European Commission then it will reach out to whichever country in which your business resides, to enforce any and all penalties and or fines.
The Future of Data Collection In America
Americans are becoming more aware and more concerned about how their personal data is being collected and managed, whether it’s data collected through online searches or data collected by our social media platforms. Bills providing similar protections to the GDPR have been proposed and/or enacted in multiple states. California has passed similar laws to protect its citizens known as the California Privacy Protection Act (CalOPPA) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Do You Have Questions About GDPR Compliance?
We strongly suggest that you consult one of our Oklahoma or Kansas business attorneys if you are unsure whether your company is subject to or complies with the GDPR. There are numerous provisions of the GDPR that could apply to your company. Do not leave anything to chance when you set up your business. Careful planning in the beginning stages of a business can help you save money and prevent problems in the future. Contact Davis Business Law today to speak to an Oklahoma or Kansas Corporate Attorney for more information.

Matthew Davis
Business Lawyer/CEO
The content on this page has been reviewed and approved by Matthew Davis: CEO of Davis Business Law.